Contact Us
Reflow Process
Our production covers a wide range of industries and products in China and abroad. To help you design and produce
Reflow Process
Reflow soldering is a common surface mount technology used to solder surface mount devices (SMD) to circuit boards. In the reflow soldering process, the solder paste is first applied to the board, then the SMD is placed on the paste, and finally the board is heated through a certain temperature curve to melt the paste and solder the SMD to the board.
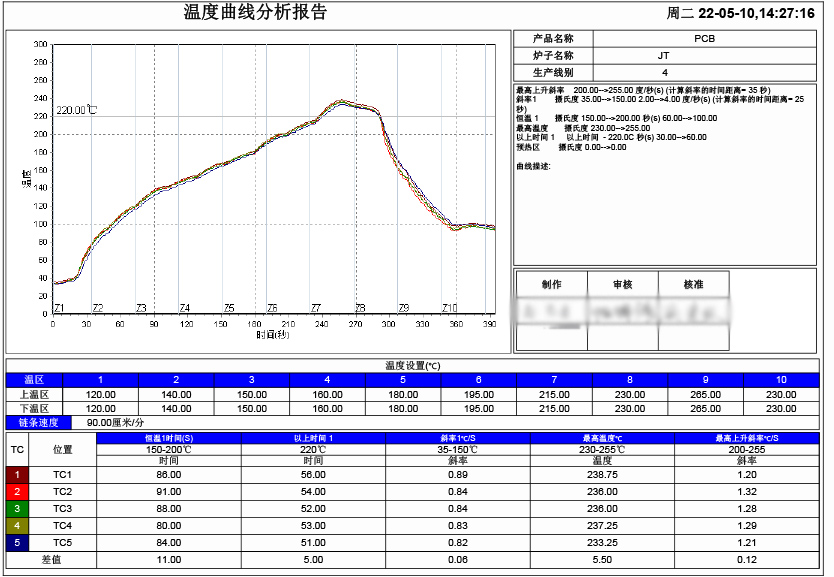
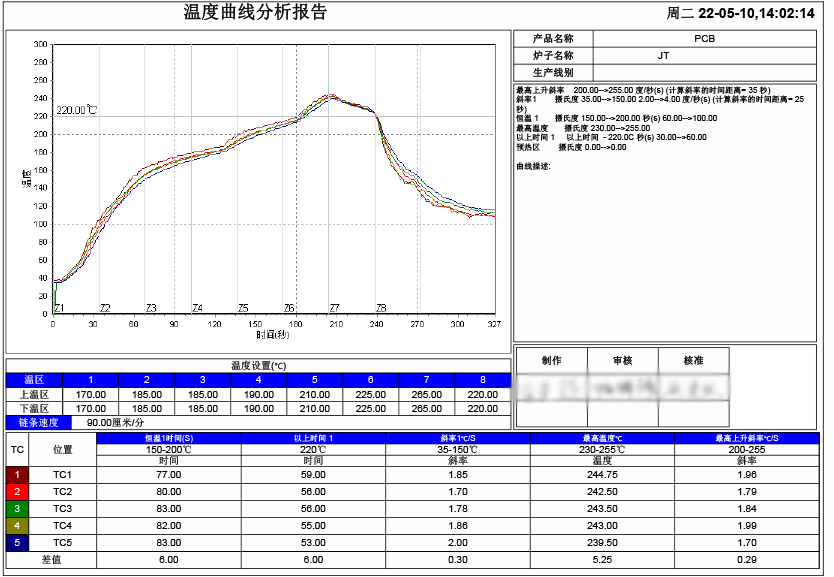
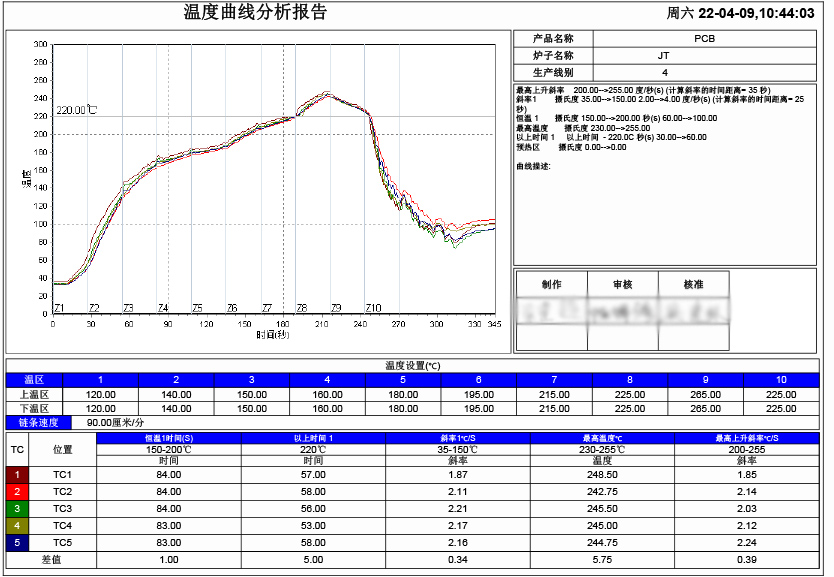
Reflow soldering is usually divided into four stages: preheat, constant temperature, reflow and cooling. The preheat stage is used to heat the board and surface mount components to a pre-determined temperature range of solder temperature, typically 100°C150°C. The constant temperature stage heats the board and surface mount components to the maximum solder temperature, typically 220°C250°C, and holds them for a period of time. Reflow stage heats the soldering area to the melting temperature of the solder paste, usually 240°C to 260°C, and holds it for a period of time to melt the paste and form solder joints. The cooling stage cools the board and surface mount components to room temperature to form a stable solder joint structure.
Reflow soldering technology has the advantages of high efficiency, high quality, and high automation, and has been widely used in the electronics manufacturing industry.
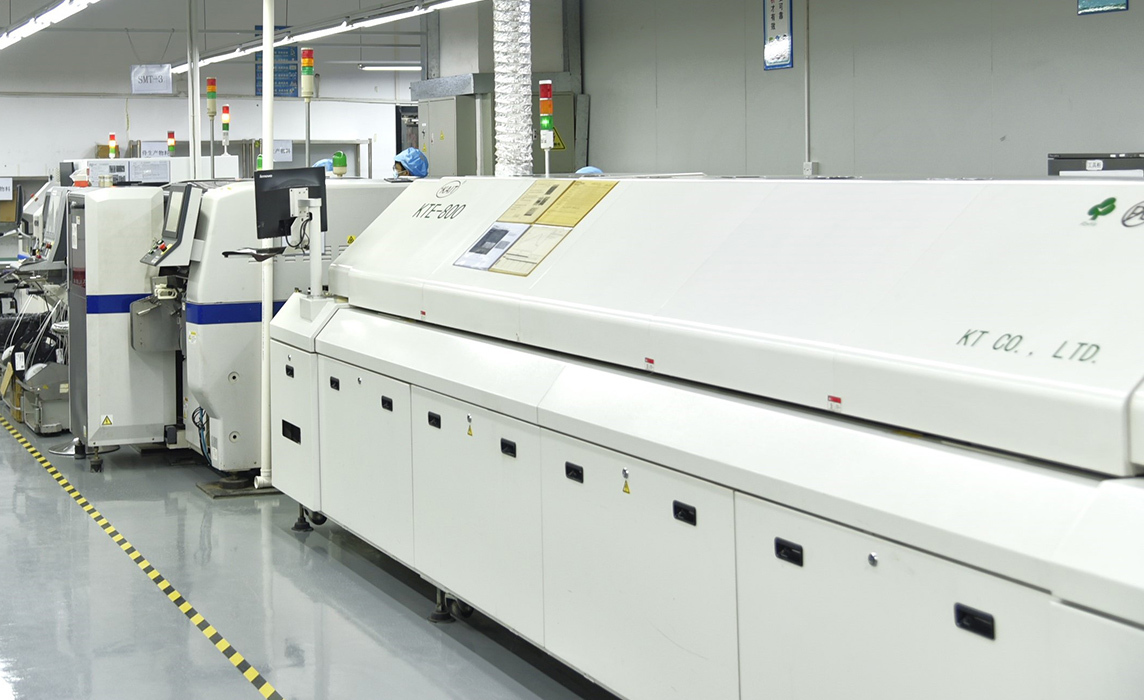
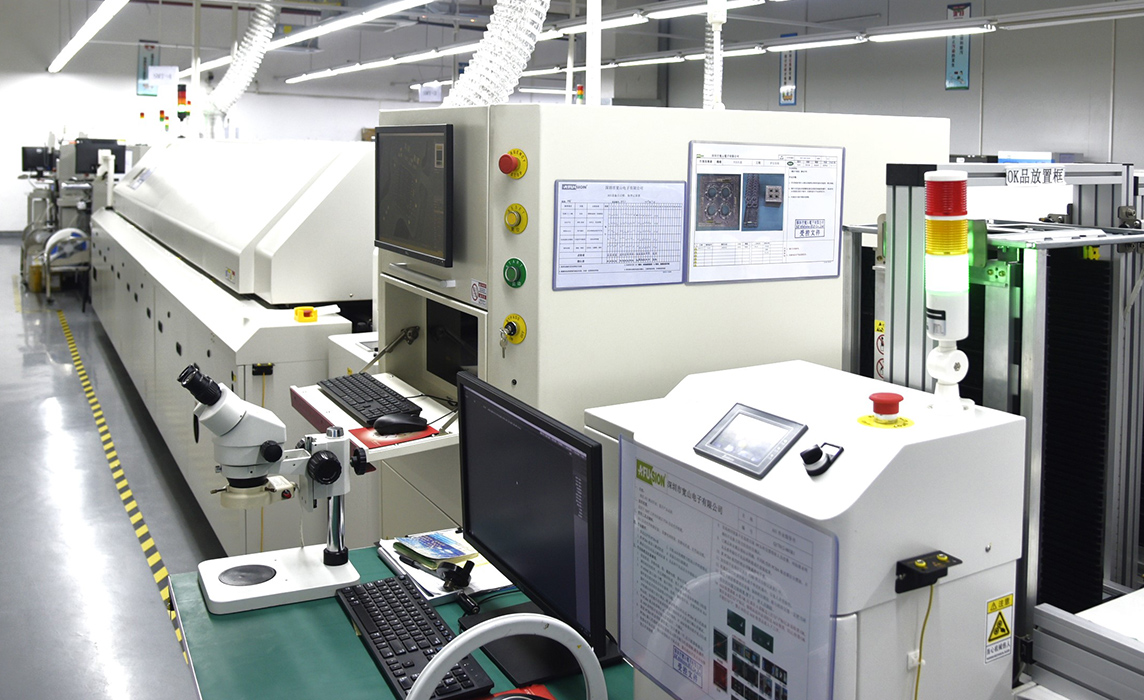
Equipment Show


Temperature Curve Analysis Report